Energy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{banner|There is currently no way to power the world without fossil fuels. Until major technological breakthroughs happen, we have to consume less.<br /><small>This is not as hard as it sounds.</small>}} | |||
This page is about energy in 2 main forms: '''fuel and electricity'''. | This page is about energy in 2 main forms: '''fuel and electricity'''. | ||
==Energy supply== | ==Energy supply== | ||
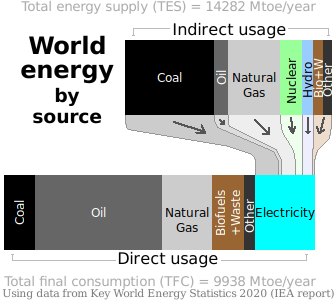
===The majority of energy comes from [[fossil fuels]] which cause [[climate change]].=== | ===The majority of energy comes from [[fossil fuels]], which are the main cause of [[climate change]].=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
[[File: energy-usage-by-source.png|border|alt=Energy sources]] | [[File: energy-usage-by-source.png|border|alt=Energy sources]] | ||
=== | ===What about other energy sources?=== | ||
{|class="wikitable" | |||
{| class= | |||
!Energy source | !Energy source | ||
! | !Main limitation | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[ | |[[Hydro]] | ||
| | |Geography | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[ | |[[Nuclear]] | ||
| | |Needs uranium-235 which is too scarce* | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Solar]] | |[[Solar]] | ||
| | |Too many rare metals needed* | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Wind]] | |[[Wind]] | ||
| | |Geography | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[ | |[[Biofuel]] | ||
| | |Causes [[deforestation]] and [[global hunger]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[ | |[[biomass waste|Waste]] | ||
|Limited supply | |Limited supply | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[ | |[[Geothermal]] | ||
| | |Geography. In most parts of the world, it's only suited for [[heating]] and [[cooling]]. | ||
|} | |} | ||
Solar and wind are also limited by [[energy storage]].* | |||
<nowiki>*</nowiki>Limitations marked with an asterisk (*) are possible to overcome '''with the right innovations'''. | |||
More details are found on the wikipage of each energy source. Links are in the table. | |||
==Energy demand== | ==Energy demand== | ||
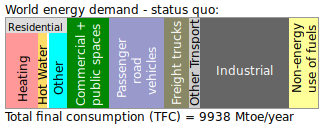
What is energy mainly used for? Some basic categories:<br /> | |||
[[File: energy-demand-status-quo.png|border|alt=Energy uses]]<br /> | [[File: energy-demand-status-quo.png|border|alt=Energy uses]]<br /> | ||
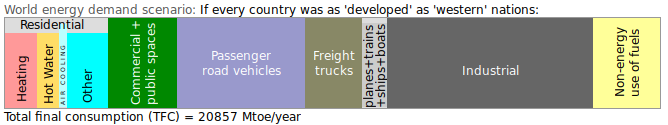
Most of the world is currently living in '''poverty'''. Suppose every country was as ''developed'' as ''western'' countries: [[energy demand scenarios|Global energy demand could be more than '''double''']]: | |||
[[File: energy-demand-if-developed.png|border|alt=Energy demand if everyone lived a first-world lifestyle]] | |||
This is far beyond today's green energy capacity. | |||
===Transportation sector=== | |||
Energy demand would be different if vehicles didn't run on gasoline or diesel. In general, we'd need less energy to ''power'' the vehicles but more energy to ''manufacture'' them (and later ''recycle'' them at their end of life). Overall, total energy demand would be ''slightly'' less. See [[electric vehicles/energy|this chart]]. | |||
There are currently some serious roadblocks to making this happen. Read the page on [[electric vehicles]] to see how they could maybe be overcome. | |||
It's quite possible that there's ''no good solution'' for electric vehicles, and the only way to make transportation sustainable is for people to ''drive less''. This goes against suburban culture, but it isn't as hard as it sounds. Some things that would help: | |||
* [[Walkability]] - organizing neighborhoods so things are in optimal locations, so people don't have to drive as far as often. | |||
* [[Public transit]] done right. <small>Yes, there are plenty of ways for it to be done wrong!</small> | |||
* Working from home - only suited for ''some'' types of work, of course. | |||
* [[Carpooling]] - yes, this takes some effort and coordination. | |||
===Reducing energy demand=== | |||
A common misconception is that "saving energy" is ''mostly'' about turning off lights, turning off computers, etc. Those actions are worthwhile but don't actually make a ''big'' difference. '''Other''' personal lifestyle choices do. | |||
More than half of energy demand {{x|commercial vehicles + industrial/manufacturing + ''some'' commercial spaces}} is affected by '''what people buy''', and '''how much''' of it. | |||
''More information on this soon.'' | |||
Revision as of 15:08, 19 January 2023
This is not as hard as it sounds.
This page is about energy in 2 main forms: fuel and electricity.
Energy supply
The majority of energy comes from fossil fuels, which are the main cause of climate change.
What about other energy sources?
| Energy source | Main limitation |
|---|---|
| Hydro | Geography |
| Nuclear | Needs uranium-235 which is too scarce* |
| Solar | Too many rare metals needed* |
| Wind | Geography |
| Biofuel | Causes deforestation and global hunger |
| Waste | Limited supply |
| Geothermal | Geography. In most parts of the world, it's only suited for heating and cooling. |
Solar and wind are also limited by energy storage.*
*Limitations marked with an asterisk (*) are possible to overcome with the right innovations.
More details are found on the wikipage of each energy source. Links are in the table.
Energy demand
What is energy mainly used for? Some basic categories:
Most of the world is currently living in poverty. Suppose every country was as developed as western countries: Global energy demand could be more than double:
This is far beyond today's green energy capacity.
Transportation sector
Energy demand would be different if vehicles didn't run on gasoline or diesel. In general, we'd need less energy to power the vehicles but more energy to manufacture them (and later recycle them at their end of life). Overall, total energy demand would be slightly less. See this chart.
There are currently some serious roadblocks to making this happen. Read the page on electric vehicles to see how they could maybe be overcome.
It's quite possible that there's no good solution for electric vehicles, and the only way to make transportation sustainable is for people to drive less. This goes against suburban culture, but it isn't as hard as it sounds. Some things that would help:
- Walkability - organizing neighborhoods so things are in optimal locations, so people don't have to drive as far as often.
- Public transit done right. Yes, there are plenty of ways for it to be done wrong!
- Working from home - only suited for some types of work, of course.
- Carpooling - yes, this takes some effort and coordination.
Reducing energy demand
A common misconception is that "saving energy" is mostly about turning off lights, turning off computers, etc. Those actions are worthwhile but don't actually make a big difference. Other personal lifestyle choices do.
More than half of energy demand
More information on this soon.