File:fossil-fuels-ghg-by-energy.png: Difference between revisions
(Greenhouse gas emissions of the 3 fossil fuels, per unit of energy) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Summary == | == Summary == | ||
[[Greenhouse gas]] emissions of the 3 fossil fuels, per unit of [[energy]] | [[Greenhouse gas]] emissions of the 3 [[fossil fuels]], per unit of [[energy]]. | ||
== Numbers == | |||
Emissions measured in [[Term:CO2eq|CO<sub>2</sub>eq]] per unit of thermal energy, for each fuel: | |||
{{dp | |||
|<nowiki>coal.ghg_by_energy</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>95.35 kg / million btu</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>CO2 emissions of burning coal</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>https://www.eia.gov/environment/emissions/co2_vol_mass.php</nowiki> | |||
}} | |||
{{dp | |||
|<nowiki>gasoline.ghg_by_energy</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>71.30 kg / million btu</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>CO2 emissions of burning gasoline</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>https://www.eia.gov/environment/emissions/co2_vol_mass.php</nowiki> | |||
}} | |||
{{dp | |||
|<nowiki>natural_gas.ghg_by_energy</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>53.07 kg / million btu</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>CO2 emissions of burning natural gas</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>Does not include the fugitive methane emissions from unburned fuel. Those vary by how the gas is burned.</nowiki><br /><nowiki> | |||
</nowiki><br /><nowiki> | |||
https://www.eia.gov/environment/emissions/co2_vol_mass.php</nowiki> | |||
}} | |||
{{dp | |||
|<nowiki>usa.natural_gas.fugitive_ghg</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>176.1 million tonnes / year</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>Greenhouse gas CO2eq of fugitive methane leaks from all natural gas infrastructure in the USA</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)</nowiki><br /><nowiki> | |||
Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990-2014</nowiki><br /><nowiki> | |||
https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/inventory-us-greenhouse-gas-emissions-and-sinks-1990-2014</nowiki><br /><nowiki> | |||
2016 Complete Report (PDF)</nowiki><br /><nowiki> | |||
Using data from 2014</nowiki> | |||
}} | |||
{{dp | |||
|<nowiki>usa.natural_gas.energy</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>27.9 quadrillion btu / year</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>U.S. energy consumption from natural gas combustion only</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)</nowiki><br /><nowiki> | |||
Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990-2014</nowiki><br /><nowiki> | |||
https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/inventory-us-greenhouse-gas-emissions-and-sinks-1990-2014</nowiki><br /><nowiki> | |||
2016 Complete Report (PDF)</nowiki><br /><nowiki> | |||
Datapoint was found on page 115, from pie chart and line graph, using data from 2014</nowiki> | |||
}} | |||
{{dp | |||
|<nowiki>natural_gas.fugitive_ghg_by_energy</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>usa.natural_gas.fugitive_ghg / usa.natural_gas.energy</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>Fugitive emissions (CO2eq) of natural gas, per unit energy</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>Average based on US datapoints.</nowiki> | |||
}} | |||
{{calc | |||
|coal.ghg_by_energy | |||
|kg / million btu | |||
| | |||
|Coal: | |||
}} | |||
{{calc | |||
|gasoline.ghg_by_energy | |||
|kg / million btu | |||
| | |||
|Oil (gasoline is the most popular fuel obtained from crude oil): | |||
}} | |||
{{calc | |||
|natural_gas.ghg_by_energy + natural_gas.fugitive_ghg_by_energy | |||
|kg / million btu | |||
| | |||
|Natural gas, which also has ''fugitive emissions''{{x|Natural gas is mostly methane (CH<sub>4</sub>) which is ''also'' a [[greenhouse gas]]. So when any unburned fuel leaks into the atmosphere (gas leaks), it also contributes to climate change too.}} taken into account here: | |||
}} | |||
Latest revision as of 23:43, 31 July 2023
Summary
Greenhouse gas emissions of the 3 fossil fuels, per unit of energy.
Numbers
Emissions measured in CO2eq per unit of thermal energy, for each fuel:
coal.ghg_by_energy
95.35 kg / million btu
CO2 emissions of burning coal
https://www.eia.gov/environment/emissions/co2_vol_mass.php
gasoline.ghg_by_energy
71.30 kg / million btu
CO2 emissions of burning gasoline
https://www.eia.gov/environment/emissions/co2_vol_mass.php
natural_gas.ghg_by_energy
53.07 kg / million btu
CO2 emissions of burning natural gas
Does not include the fugitive methane emissions from unburned fuel. Those vary by how the gas is burned.
https://www.eia.gov/environment/emissions/co2_vol_mass.php
https://www.eia.gov/environment/emissions/co2_vol_mass.php
usa.natural_gas.fugitive_ghg
176.1 million tonnes / year
Greenhouse gas CO2eq of fugitive methane leaks from all natural gas infrastructure in the USA
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990-2014
https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/inventory-us-greenhouse-gas-emissions-and-sinks-1990-2014
2016 Complete Report (PDF)
Using data from 2014
Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990-2014
https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/inventory-us-greenhouse-gas-emissions-and-sinks-1990-2014
2016 Complete Report (PDF)
Using data from 2014
usa.natural_gas.energy
27.9 quadrillion btu / year
U.S. energy consumption from natural gas combustion only
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990-2014
https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/inventory-us-greenhouse-gas-emissions-and-sinks-1990-2014
2016 Complete Report (PDF)
Datapoint was found on page 115, from pie chart and line graph, using data from 2014
Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990-2014
https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/inventory-us-greenhouse-gas-emissions-and-sinks-1990-2014
2016 Complete Report (PDF)
Datapoint was found on page 115, from pie chart and line graph, using data from 2014
natural_gas.fugitive_ghg_by_energy
usa.natural_gas.fugitive_ghg / usa.natural_gas.energy
Fugitive emissions (CO2eq) of natural gas, per unit energy
Average based on US datapoints.
Coal: (calculation loading)
Oil (gasoline is the most popular fuel obtained from crude oil): (calculation loading)
Natural gas, which also has fugitive emissions
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 23:30, 31 July 2023 | 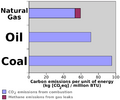 | 944 × 784 (44 KB) | Elie (talk | contribs) | Greenhouse gas emissions of the 3 fossil fuels, per unit of energy |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: