Fossil fuels
Fossil fuels include coal, oil, and natural gas. They occur naturally in the Earth, and can be burned for energy. They currently provide over 80% of the world's energy, but at a heavy environmental cost.
Terminology
- Natural gas is sometimes referred to as just gas. Not to be confused with gasoline.
- Crude oil is also known as petroleum, and it can be refined into oil products such as gasoline and diesel.
Usage as an energy source
Climate change
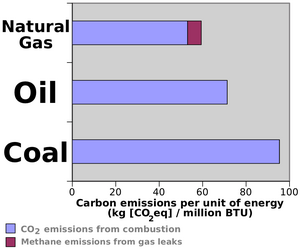
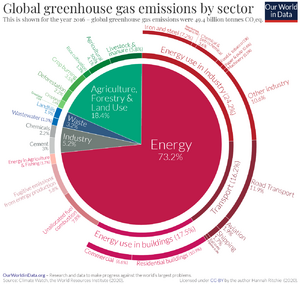
Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of climate change, due to the CO2 it releases into the atmosphere.
And it's unlikely that carbon capture and storage would ever be able to store that much CO2 in the ground.
Other pollution
Burning fossil fuels releases more than just CO2.
- Exhaust from cars and trucks
- Exhaust from coal power plants
These contain particles that are harmful to people and ecosystems.[ELABORATION needed]
Mitigation
- Cars and trucks already have catalytic converters that eliminate some of this pollution - but not all of it.
- For coal power plants, newer technologies could avoid most of this pollution (but not the CO2 that causes climate change).
Scarcity
Oil reserves are expected to run out in less than a century, by most estimates. Coal and natural gas are similar. [QUANTIFICATION needed]
Fossil fuels are not considered renewable
Oil | Energy economics | Home - BP
www.bp.com › energy-economics › statistical-review-of-world-energy › oil
Source: Key World Energy Statistics 2020 (IEA report)
Last updated in 2023
Globally, per person, there is about 31 tonnes of oil (recoverable) somewhere in the Earth ['''] (calculation loading) . Average production is about 1.5 kg/day per person ['''] (calculation loading) . Rich countries consume a lot more, poor countries use a lot less.
Non-energy usage
- Fossil fuels are also used in making plastic, most of which is disposable.
- Other uses include making thousands of different chemicals. This together adds up to only a small fraction of fossil fuel consumption, and does not contribute significantly to climate change. [QUANTIFICATION needed]